Personalisation: we’ve all heard it, but what exactly is it and how can it help ecommerce brands grow?
According to Hostingers Ecommerce statistics there are 24 million ecommerce websites out there and the number is increasing each day. I don’t know about you but that’s a huge number.
With the number of ecommerce websites growing it becomes that much more important to stand out from your competitors. And this is where personalization of your ecommerce website comes in.
Ecommerce Personalization is becoming a new thing. And very few ecommerce brands are jumping on this. Think about it, would you rather get a simple assorted chocolate box as a gift or a personalised assorted chocolate box with all the flavours of chocolates that you like. It’s obvious isn’t it? It would be a personalised chocolate box.
Making your ecommerce store personalised makes consumers like your brand and remember it more often and and in return they are most likely transact more, which would lead to greater growth in revenue.
91% of consumers are more likely to shop with brands who recognize, remember, and provide them with relevant offers and recommendations. -Accenture survey, 2018
Let’s deep dive into finding the nitty gritties of personalization for an ecommerce brand.
What Is Personalisation In Ecommerce?
Let’s start with simple things – “What is personalization?”
Let me take an example – If a customer has recently purchased a book about gardening, they may be recommended other books on gardening or related topics to gardening. In essence this is personalization.
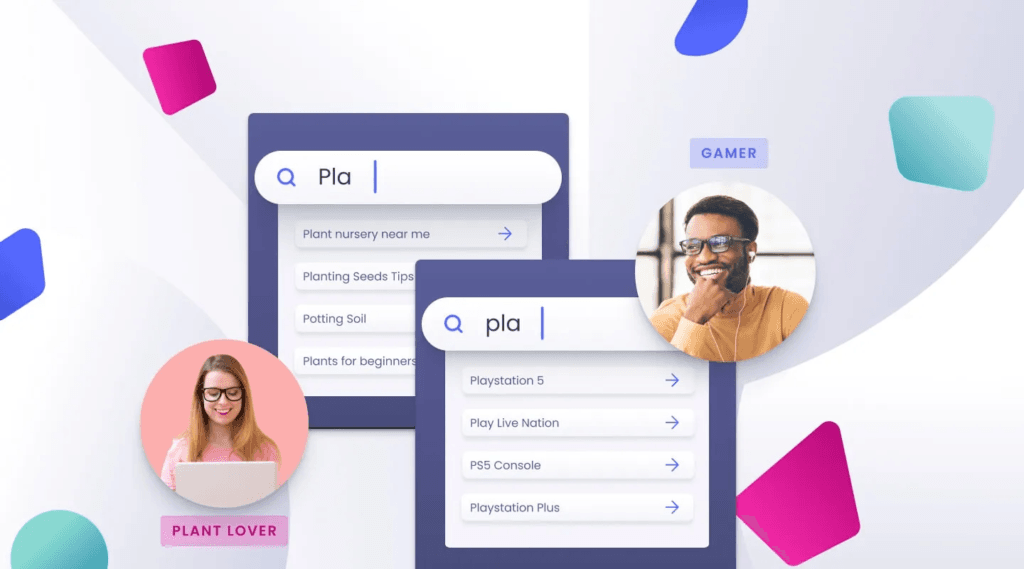
But when it comes to ecommerce business personalization, things start to get complicated.
But Why is Ecommerce Personalisation Complicated?
When a user browses an ecommerce website they visit multiple products and buy products and to add on to this each user has a different behaviour and different way of thinking. This makes it difficult to recommend the right product.
This is where modern tech comes in that collects, analyses large amounts of data, often utilising machine learning algorithms and other advanced technologies, to understand and predict an individual’s behaviors, interests, and needs.
A real good example of personalization would be amazon, based on your buying behaviour and the products that you buy amazon recommends products that you might need.
Another good example would be spotify, the advanced algorithm learns the type of music you are listening to and recommends a curated list of songs that you may like.
Why Is Personalisation Important For Ecommerce Businesses?
You don’t currently use personalization but things are working for you, and why should I choose personalization rather I would focus on inventory or new products or push more money into marketing to get more customers. – These are probably some of the questions that may pop into your head but trust me I’ve seen how sales can grow with changes on the website.
89% of eCommerce companies are investing in personalization. – Hostingers Ecommerce statistics
If this data is not enough for one to take action and start implementing personalization strategies for your ecommerce store, then I don’t know what will. Customers in today’s modern tech lead environment expect brands to listen to them and understand how they function and realise needs even before they do and this is where ecommerce personalization comes into play.
Different Types Of Personalization In Ecommerce
Couple of years back personalization would have been a daunting task, but tech being so accessible, today, there are a number of Saas providers present out there to help with this challenge alone.
Using simple marketing automation tools, ecommerce personalization has become affordable for everyone and you don’t need to be tech savvy to get things started, you can find what is working for you and then invest in it.
Different data points one can look at while personalising of the ecommerce store
- Serving dynamic content for customers based on their
- Location or IP – Showing content based on users location like currency, shipping details, and language.
- Device used – Leveraging which device the user is coming through have conversion optimised specific landing pages for mobile, tabs and PC.
- Traffic source – Depending on where the customers are coming from show them different landing pages. For ex: If there are users coming from paid ads show them a similar kind of solution that has made them click the ad.
- Demographics – Use age, gender to your advantage to curate landing pages
- New / Old Customers– Different communication for different customer cohorts
- Dynamic product: Depending of the type of customer show different/relevant products
- For ex: If we know that the customer is new we can show the bestselling products that most people on the website buy.
- Dynamic pricing: Depending on the country or the region the customer is coming from the currency and the price can be changed. If you want to move one step further you can give the pricing algorithm a shot. These algorithms work on competitive price points, historic sales data and market demand, these might not be viable for specific ecommerce brands but it is worth looking into.
- Dynamic content: Dynamic content blocks show related products or last viewed products. These can help build recall and encourage customers to transact. This is a great way to show exclusive offers and communicate with customers on a more personal level.
Best Practices For Personalisation In Ecommerce
A big part of personalization rests on collecting user data, so always be sure to keep your customers in loop of the type of data that you’ll be collecting and how you’ll be using it.
- Customer experience: Personalization for an ecommerce brand can be tech heavy, so always keep a check that you don’t compromise basic things like user experience and page load speeds.
- DSTC (Data privacy, Security, Transparency and Consent): Always respect user privacy and make sure your customers are in loop of the data that you collect.
- Accuracy of data: Clean and validate your data that you collect to avoid incorrect or irrelevant personalised experience.
- Avoiding over-personalization: While personalization is important, don’t go overboard and over-personalize it. Balance personalization with respect to your customers preference and privacy.
- Consistency across channels: Be sure to have the same experience across channels. Make sure that the customer has the same kind of experience and communication across the website, email or even a mobile app.
- Scalability: Plan for scalability as your customer base grows and the volume of data increases. Make sure your infrastructure and systems can handle the demands of personalization without sacrificing performance or security.
Common Mistakes To Avoid In Ecommerce Personalisation
I am not going to lie but the cost of personalization can be expensive, hence choosing the right tools and the right strategies becomes crucial and avoiding these common mistakes can help get you a long way.
- Lack of relevance: Ecommerce personalization should be based on accurate and relevant data. Avoid making assumptions or delivering personalised experiences that are not aligned with the customer’s actual preferences or behaviour. Invest in collecting and analysing accurate data to provide meaningful personalization.
- Overwhelming customers: Be cautious not to overwhelm customers with excessive personalization. Bombarding them with too many recommendations, pop-ups, or notifications can lead to a negative user experience. Find the right balance between customization and simplicity.
- Ignoring customer privacy concerns: Respecting customer privacy is crucial. Failing to obtain proper consent, being unclear about data usage, or not providing options for customers to control their personalization settings can erode trust. Prioritise data security and ensure compliance with privacy regulations.
- Lack of testing and optimization: Ecommerce personalization strategies should be regularly tested and optimised. Failing to analyse the performance of your personalization efforts can result in missed opportunities for improvement.
- Limited data collection: Relying on limited or insufficient customer data can limit the effectiveness of personalization. Strive to collect comprehensive data that encompasses multiple touchpoints and customer interactions.
- Lack of cross-channel consistency: Inconsistent ecommerce personalization experiences across different channels can create confusion and frustration. Strive for consistency in personalised content, recommendations, and messaging across your website, mobile app, email campaigns, and social media platforms.
- Neglecting the human touch: While automation and algorithms play a crucial role in ecommerce personalization, don’t overlook the importance of human interaction. Personalization should not feel robotic or devoid of human touch.
- Failing to consider context: Personalization should take into account the context in which the customer is interacting with your website or app. Consider factors such as location, time of day, device, or browsing behaviour to deliver contextually relevant experiences.
- Neglecting non-personalized experiences: While personalization is valuable, don’t overlook the importance of non-personalized experiences. Some customers may prefer a more general browsing experience or may be new to your website and not yet have sufficient data for personalization.
Tools That Can Help Ecommerce Personalisation
Creating personalization algorithms can be time consuming and expensive but there are several tools out that can help with personalization and some are rather easy to start off with.
Remember to evaluate each tool’s features, pricing, and compatibility with your existing systems to choose the ones that best fit your business needs.
- Customer Data Platforms (CDPs): CDPs help collect, unify, and organise customer data from various sources into a single, comprehensive ecommerce dashboard. These tools enable you to create detailed customer profiles and segments, which are essential for personalised experiences.
Examples of CDPs include Segment, Tealium, and Optimizely. - Marketing Automation Platforms: These platforms allow you to automate ecommerce personalised marketing campaigns and communications based on customer behaviour and segmentation. They typically include features such as email marketing automation, customer journey mapping, and dynamic content.
Examples of marketing automation platforms include Marketo, HubSpot, and Salesforce Marketing Cloud. - Personalization Engines: Ecommerce personalization engines utilise machine learning algorithms to deliver tailored experiences to individual customers. They analyse customer data, behaviour, and preferences to generate personalised product recommendations, content, and offers.
Examples of ecommerce personalization engines include Dynamic Yield, Evergage, and Qubit. - Content Management Systems (CMS): A CMS with ecommerce personalization capabilities enables you to create and manage personalised content on your website. It allows you to display different content variations to different segments of your audience.
Examples of CMS platforms with personalization features include WordPress with personalization plugins, Sitecore, and Adobe Experience Manager. - A/B Testing Tools: A/B testing tools help you test and optimise different versions of your website or app to determine the most effective personalization strategies. They allow you to experiment with different content, layouts, and features to improve conversion rates and user engagement.
Examples of A/B testing tools include Optimizely, Google Optimise. - Recommendation Engines: Recommendation engines analyse customer data and behaviour to generate personalised ecommerce product recommendations. These tools can be integrated into your ecommerce platform to provide relevant cross-sell, up-sell, and related product suggestions.
Examples of recommendation engines include Barilliance, Nosto, and RichRelevance. - Analytics Tools: Analytics platforms provide insights into customer behaviour, engagement, and conversions. They help you understand the effectiveness of your ecommerce personalization efforts and identify areas for improvement.
Examples of analytics tools include Google Analytics, Adobe Analytics, and Mixpanel. - CRM Systems: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems help you manage and track customer interactions and relationships. They store customer data and enable personalised communication and customer service.
Examples of CRM systems include Salesforce, HubSpot CRM, and Zoho CRM.
Conclusion
Providing a personalised ecommerce experience has become an essential practice for businesses aiming to attract and retain customers while staying ahead of competitors. To deliver personalised experiences, it is vital to gather customer data, segment your user base, analyse their behaviours and preferences, and create tailored purchasing journeys for each segment.
By adopting personalisation, businesses can enhance customer engagement, improve conversion rates, and foster long-term customer loyalty.



![[TEMPLATE] Choosing the Right Code Collaboration Tool: Streamline Your Tool Selection Process 7 template to choose the right collaboration tools](https://theglobalthinking.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/template-collobaration-tools-120x120.png)


